Overview
TuitionConnect is an integration of address book and task manager optimized to be used by private tuition teacher for managing their busy schedule efficiently and effectively.
Summary of contributions
-
Major enhancement: added *scheduling features
-
What it does: allows the users to organize their activities neatly by creating and deleting tasks. Also, allows users to browse through their schedule with ease using the find and sort utilities.
-
-
Minor enhancements
-
Implemented tutee listing, filtering and sorting features.
-
-
Code contributed: [Functional code] [Test code]
-
Other contributions:
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
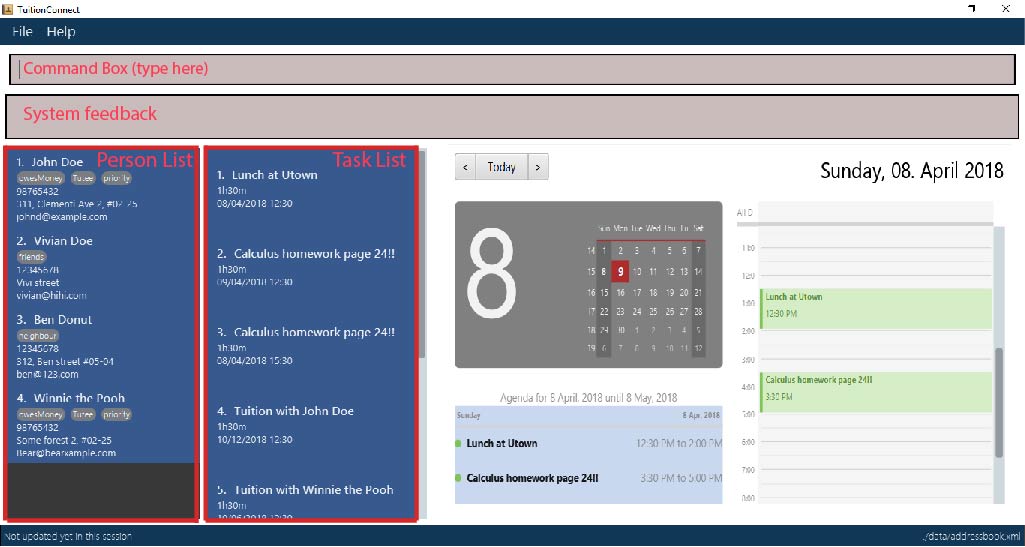
Concepts Introduction
-
Contact : This refers to both the tutee and person.
-
Tutee : This refers to the students you are teaching. Adding a student as tutee requires specific tutee details to be provided. By doing so, it will be easier to organize your contacts using our special features.
-
Person : Other contacts which are not tutee.
-
Tutee Details : These are details that are only owned by tutees, which include tutee’s education level, grade, subject and school.
-
Task : This refers to the activities you want to add into your 'to-do-list'.
Type of Task:-
Tuition task: Teaching a specified tutee in contact list.
-
Personal task: Non-tuition activity.
-
-
Address Book : This refers to the list of contacts located on the most left side of the app.
-
Task List / Schedule : these terms are used interchangeably to refer to the list of tasks located in the middle of the app.
Adding a tuition task: addtuition
Adds a task to TuitionConnect’s schedule
Using Command Word:
Format: `addtuition TUTEE_INDEX DATE TIME DURATION [DESCRIPTION]
Examples:
-
addtuition 1 10/05/2018 09:00 1h30m Calculus homework page 24 -
addtuition 1 31/12/2018 16:00 0h30m
Sorting tasks by category: sorttaskby
Sorts your displayed task list according to a specified category in ascending order.
Using Command Word:
Format: sorttaskby CATEGORY
Using Command Alias:
Format: stb CATEGORY
Example:
-
sorttaskby Month
sorts tasks by month in increasing order.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
Model component
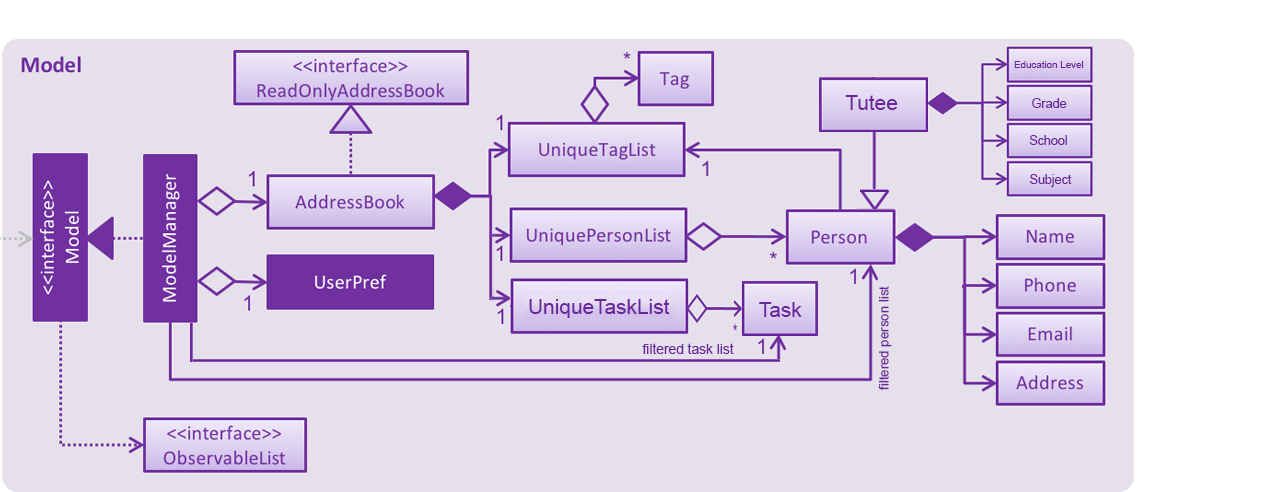
API : Model.java
The Model,
-
stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. -
stores the Address Book data.
-
exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Person>andObservableList<Task>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. -
does not depend on any of the other three components.
Storage component
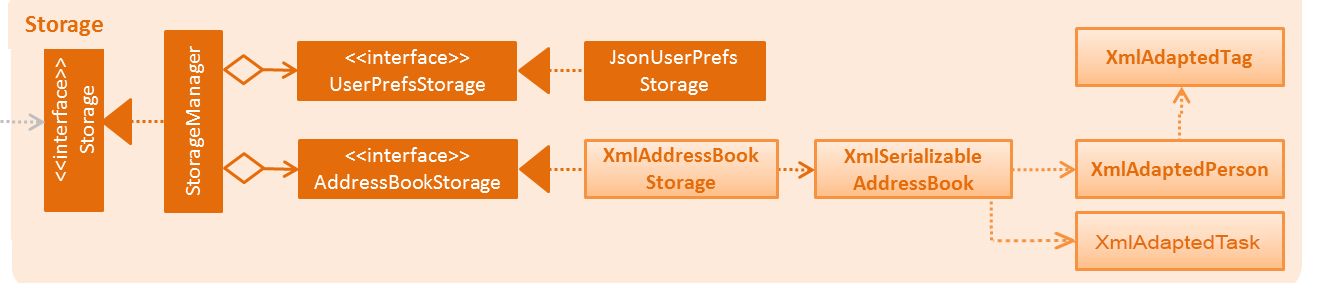
API : Storage.java
The Storage component,
-
can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. -
can save the Address Book data in xml format and read it back.
Sort Person Command
Reason for Implementation
As the amount of contacts stored grows, it would be harder to browse the address book. Hence, Sort Person Command is created to ease users’s experience in organizing their address book.
How it is implemented
The following sequence diagram shows the general idea of how sort person command works:
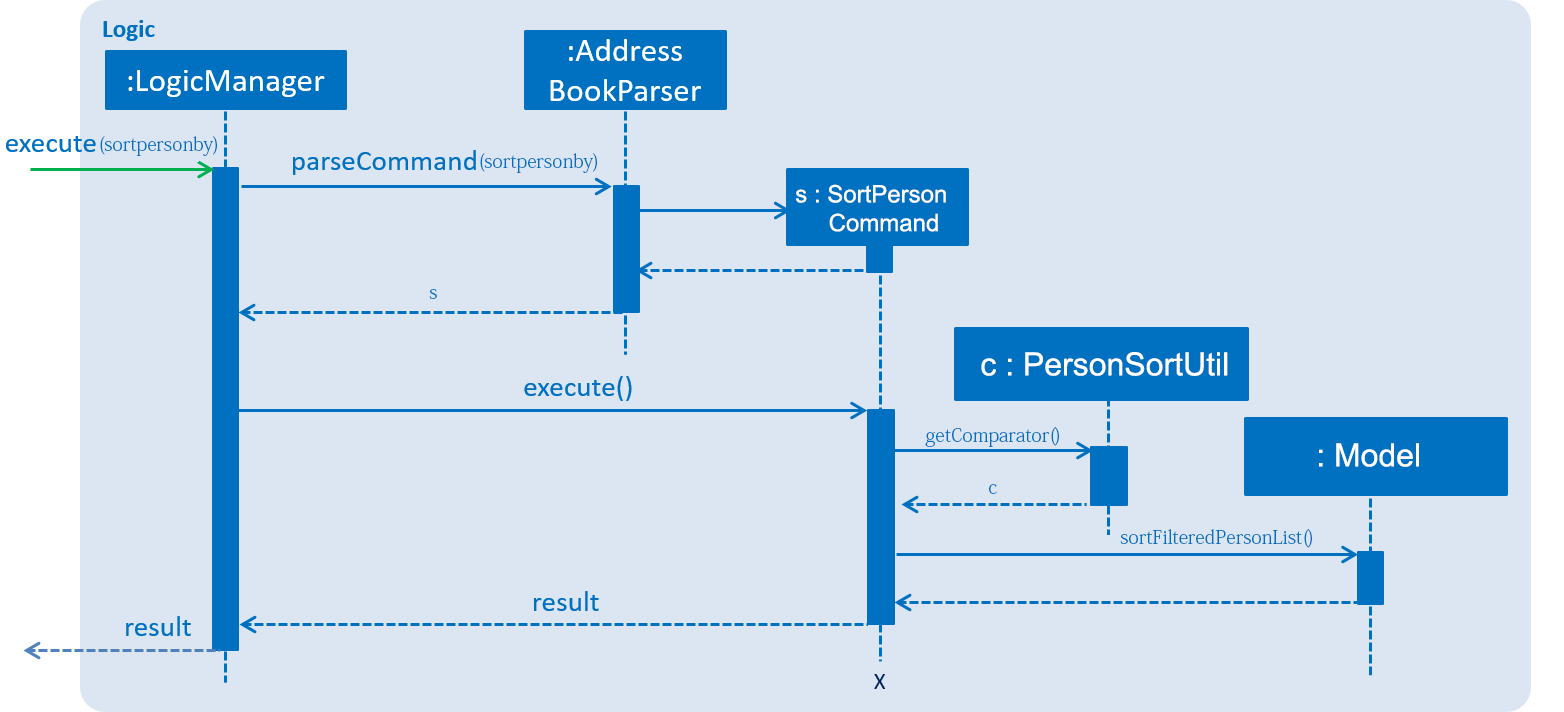
As shown in the sequence diagram, the Logic command’s call for execution results in Sort Person command to request for a Comparator object from PersonSortUtil class. A comparator object is required since the sorting implementation utilizes JavaFX8’s SortedList class. (Refer to https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/javafx/api/javafx/collections/transformation/SortedList.html for more information) Here, PersonSortUtil class is responsible in providing a suitable comparator that matches the sorting behaviour requested by the user. Upon receiving the comparator, SortPersonCommand calls the sortFilteredPersonList() method which utilises a SortedList object to perform the sorting.
Natural Language Identifier
Reason for Implementation
Figuring out the exact date for a tuition appointment can be tedious in some extent. Tutors would need to flip over a calendar, or to perform some
operations in the context of this app. Based on this concern, as our goal is to simplify the life of tutor,
we feel the importance of introducing a feature where tutors are able to set a tuition appointment not only by date,
but also by using common terms such as: today, next month, etc.
Current Implementation Limitation
In the current implementation, common terms (or Natural Languages) are only identifiable by the Find Task command parser.
How it is implemented
A class named NaturalLanguageIdentifier applys the singleton design pattern as the class stores a private attribute that records the current time of the system clock. As this reference time must be the same throughout the entire execution of a command, this class should only be instantiated once.
This class is responsible for identifying whether a given user input is a recognizable natural language and convert it into the desired format when applicable. In achieving this purpose, the public methods within this class are called by the command parsers that inherit Address Book parser. In general, these public methods have a certain characteristic. These methods always take in a user’s input as parameter and either return the same input if it is not recognized as a valid natural language or return a processable form of the natural language. For example, given this month (a valid natural language) as user input, the getMonthAsString() method will return April (the current month).
Valid or recognized natural languages are determined by a static list inside the NaturalLanguageIdentifier class. This list of Strings stores common terms used by tutors. If a given user input matches one of the terms in the list, that input is treated as a valid natural language.